Audio-into-image steganography by AI Team at IEEE GCCE 2019
Last July, good news arrived for the AI team of R&D Unit. After long days of waiting, the scientific report on the study of steganography by the team since April has been accepted for presentation in the IEEE Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE) 2019. The report is highly praised by the council, and it is scheduled in the OS-ICE session. After completing the content and necessary processes, in October, AI team will be having the honor of going to Osaka, Japan to attend the conference and present about this scientific report.
About IEEE GCCE 2019
IEEE GCCE is an annual international conference sponsored by IEEE Consumer Electronics Society. This conference aims towards the most recent and advanced technologies that are applicable in electronics field like: audiovisual technology, artificial intelligence and robotics, smart health care and supervision, smart house, mobile devices and embed systems, image processing, audio processing, speech processing, technologies related to entertainment and education, computing and security system.

OS-ICE is a session in the conference, related to technologies that collect and store data for Deep learning in IoT; supervised, semi-supervised and unsupervised machine learning; image processing and application, image recognition; object detection and tracking; image search and restoration; security and encryption; copy prevention and distribution right protection,...
Steganography
Steganography is data concealment, or encryption, one of the crucial techniques in information security. In a few years back, steganography has gained more popularity due to the expanding area of effect, not just within security field. Steganography aims at concealing the existence of information within the data; secret information is hidden in normal data so that the opponents cannot discover the existence of the concealed secret information.

We have been knowing and using this technology since forever, but not many know that it is steganography.
As high school kids, a lot of people must be familiar with cheating using out-of-ink pen to write on white paper, so during the exam, they can use reflected light to look at the cheat sheet, that is also steganography.
In a more dangerous case, in 2003, the CIA had to cancel more than 20 international flights with level 2 terror alert of the Homeland Security on suspicion of an enemy's headquarter has sent encrypted information to the terrorists by steganography.
The agency believed that secret messages regarding time, place and target of the terrorist attacks, including international flights were sent via the television wave by encrypting it within the images.
At present, with non-stop development of Internet and social media, billions of images and audio files are transmitted everyday. This is an advantage for steganography, making it more popular and common.
Apart from security, it is also applied in entertainment and software industry as watermarking in image, music or digital software for copyright and identity theft and copy prevention, content verification, tracking or searching illegal copies, as well as advertisement management. Big companies and corporates use it for security and product copyright by marking a licence file encrypted within a file.
Steganography is not a new field of research. There have been many research in image-in-image, video-in-video steganography, but there is yet to have any methods to conceal audio files within images effectively due to the limited data storage of the image, as well as the difference in characteristics of audio and image. Audio is an 1D chain data, while image is 3D, hence previous methods are low in quality, abnormalities can still be easily spotted after concealment, concealed data is still limited in size and storage.
Inspired by a previous research of engineer Shumeet Baluja from Google Inc in applying Deep learning in Steganography, AI team of Sun* has 2 simultaneous pathways. The first is quality of image-in-image steganography, the second is the audio characteristics to apply Deep learning in audio-in-image steganography.
Details of research

In this article, AI Team proposes Deep learning and Deep neural network for concealing secret audio in normal images. Test results have proved the effectiveness of this technique. It can be considered as the first research on using Deep learning for audio-into-image steganography.
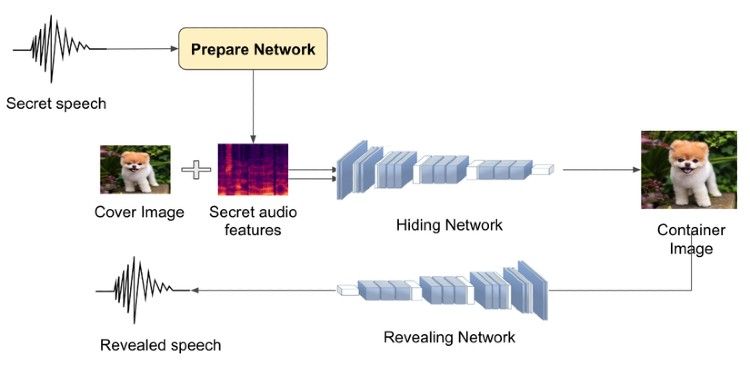
Unlike image-in-image or audio-in-audio steganography, audio-in-image steganography is much more complex, because image and audio in fact are two different formats.
Audio data is mostly in PCM-16 bit format, of value within -2^{15} đến 2^{15} - 1 while image has a value field of 0-255. This is a true challenge for the team in finding solutions.
By running many different tests, AI Team has compared many pre-processing methods, selecting the characteristics of different audio to find the most suitable method to the special requirement of the issue.
Developing team has run tests on two groups of data: Vietnamese speech data group Vivos and a public image data group on the Internet. ViVos is a public data group, including 12,420 audio files of Vietnamese voices with the sample frequencies 16kHz. Audio length ranges from 1 - 18 seconds. On the other hand, a huge amount of images from contests on Kaggle are retrieved, such as flowers, fruits, pers,... The total of retrieved image data reaches up to 24,000 images. The group divided the 2 data groups into 3 parts corresponding with the 8:1:1 proportion for training, testing and assessing.
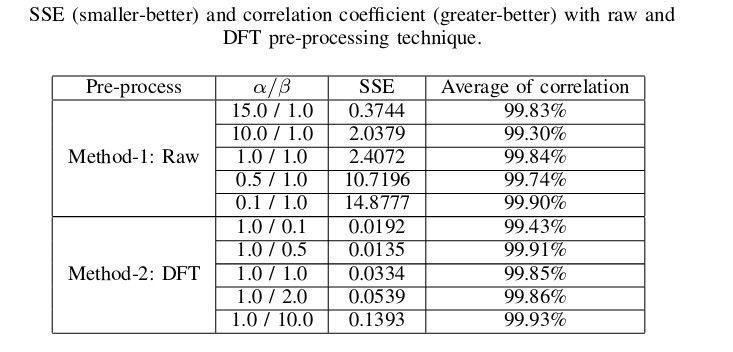
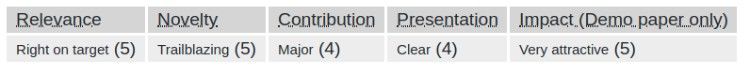
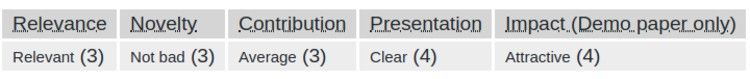
To assess the image before and after concealment, the team used the mean square of errors on 1000 images. The MSE means the total sum of each pixel, each channel of 1000 images. For audio, the team used correlation to assess the coverage, with 100% correlation with 2 identical audio. The result of the test is illustrated in the table above.
The result model can conceal one human speech record in 14 second in a 255x255 pixel image that the naked eye cannot differentiate from the original image. After recovering the audio from the image, coverage reaches 99.9%, far superior compared to the traditional technique of Least Significant Bit Encoding(LSB).

 VI
VI EN
EN